UPDATE:
Try using https://github.com/orgsync/react-list as they now have better support for the variable height use-case (see the https://github.com/orgsync/react-list#itemsizeestimatorindex-cache).
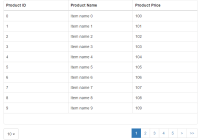
react-variable-height-infinite-scroller
An infinite scroller especially made for variable row heights (no precomputation of row height necessary).
See a Demo
Why
Because sometimes you don't know the size of the rows you're going to render before rendering
Install:
npm i --save react-variable-height-infinite-scrollerUsage:
<InfiniteScroller averageElementHeight={100} // this is a guess you make! containerHeight={600} rowToJumpTo={rowToJumpTo} // (optional) set this if you want to start/jump to a a particular row. Must be passed as a new object each time to allow for difference checking renderRow={renderRow} // function to render a row totalNumberOfRows={fakeRows.length} // an array of data for your rows /> Props
| Name | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|
containerHeight number | required | Maximum height of the scroll container |
totalNumberOfRows number | required | Length of the data array |
renderRow function | required | Function to render a row |
averageElementHeight number | (optional) 100 | This is a guess you make of what the average row height will be height. This is used to approximate how far to move the scrollbar |
| rowToJumpTo | (optional) 0 | Object of shape { row: Number }. Row you want to start with or jump to. Must be passed as a new object each time to allow for difference checking |
jumpToBottomOfRow boolean | (optional) false | By default jumping to a row jumps to the top. Set to true if you want to jump to the bottom of the row |
containerClassName string | (optional) infiniteContainer | className to apply on container |
onScroll function | (optional) no-op | Hook to call on scroll |
Methods
| Name | Description |
|---|---|
| scrollTo | Alternate way to jump to a particular row. Usage below. |
scrollTo usage*:
class MyComponent extends Component { scrollSomewhere() { this.list.scrollTo(Math.floor(Math.random() * 100)); } render() { return ( <div> Here is my list: <InfiniteScroller length={100} itemRenderer={...} ref={c => this.list = c} /> <button onClick={::this.scrollSomewhere}>Scroll Somewhere</button> </div> ); } }Taken from the demo code:
import React from 'react'; import InfiniteScroller from './InfiniteScroller.js'; function getFakeRowsWithHeights(numberOfRows) { let newFakeRows = []; for (let i = 0; i < numberOfRows; i++) { newFakeRows.push({height: Math.floor(1000 * Math.random())}); } return newFakeRows; } const Example1 = React.createClass({ getNewRandomRow(totalRows) { return {row: Math.floor(totalRows * Math.random())}; }, getInitialState() { const newNumberOfRowsToDisplay = Math.floor(Math.random() * 200); const newFakeRows = getFakeRowsWithHeights(newNumberOfRowsToDisplay); return { rowToJumpTo: null, newRowToJumpTo: this.getNewRandomRow(newFakeRows.length), fakeRows: newFakeRows, }; }, render() { const newNumberOfRowsToDisplay = Math.floor(Math.random() * 200); return ( <div style={{width: 300}} overflow="scroll"> <h3> Example 1: Random number of rows and row heights </h3> <button onClick={() => { this.setState({ rowToJumpTo: this.state.newRowToJumpTo, newRowToJumpTo: this.getNewRandomRow(this.state.fakeRows.length), }); }}> Jump to a random row: Row #{this.state.newRowToJumpTo.row} (its height is {this.state.fakeRows[this.state.newRowToJumpTo.row].height}) </button> <button onClick={() => { const newFakeRows = getFakeRowsWithHeights(newNumberOfRowsToDisplay); this.setState({ fakeRows: newFakeRows, newRowToJumpTo: this.getNewRandomRow(newFakeRows.length), }); }}> Create {newNumberOfRowsToDisplay} new rows </button> <InfiniteScroller averageElementHeight={100} // this is a guess you make! containerHeight={600} rowToJumpTo={this.state.rowToJumpTo} // (optional) set this if you want to start/jump to a a particular row. Must be passed as a new object each time to allow for difference checking renderRow={this.renderRow} // function to render a row totalNumberOfRows={this.state.fakeRows.length} // an array of data for your rows /> </div> ); }, renderRow(rowNumber) { const heightOfRow = this.state.fakeRows[rowNumber].height; return ( <div key={rowNumber} style={{height: heightOfRow, background: rowNumber % 2 === 0 ? 'red' : 'orange'}} > Height: {heightOfRow} <br/> Row Number: {rowNumber} </div> ); }, }); React.render(<Example1 />, document.getElementById('container'));Contributing
Changelog is now autogenerated. So commits have to be prefixed by one the four following prefixes to get added to the changelog:
[added]added a new feature[changed]changed an existing feature[fixed]fixed a bug[removed]removed something or a file
Run npm test to lint
#Changelog: Changelog
*(taken from "react-list")