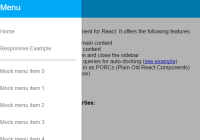
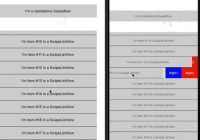
React Sidebar 

React Sidebar is a sidebar component for React 0.14+. It offers the following features:
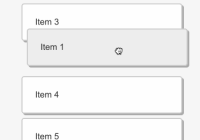
- The sidebar can slide over the main content or dock next to it.
- Touch enabled: swipe to open and close the sidebar like on a native mobile app.
- Easy to combine with media queries to show the sidebar only when there's enough screen-width (see example).
- Works on both the left and right side.
- Tiny size: <2.5kB gzipped
- MIT license
Touch specifics
The touch interaction of the React Sidebar mimics the interactions that are supported by Android apps that implement the material design spec:
- When the sidebar is closed, dragging from the left side of the screen will have the right side of the sidebar follow your finger.
- When the sidebar is open, sliding your finger over the screen will only affect the sidebar once your finger is over the sidebar.
- On release, it will call
onSetOpenprop if the distance the sidebar was dragged is more than thedragToggleDistanceprop.
Note: The sidebar touch functionality doesn't work on IOS because of the "swipe-to-go-back" feature. Therefore the functionality has been disabled on IOS.
Installation
npm install react-sidebar
If you use TypeScript, typings are available on DefinitelyTyped and can be installed with:
npm install @types/react-sidebar
Getting started
By design, React Sidebar does not keep track of whether it is open or not. This has to be done by the parent component. This allows the parent component to make changes to the sidebar and main content based on the open/docked state. An example could be to hide the "show menu" button from the main content when the sidebar is docked.
Because React Sidebar can be toggled by dragging the sidebar into its open/closed position, you will have to pass in an onSetOpen method as a prop to allow the sidebar to control the open state in the parent.
The minimum React component to integrate React Sidebar looks like this:
import React from "react"; import Sidebar from "react-sidebar"; class App extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { sidebarOpen: true }; this.onSetSidebarOpen = this.onSetSidebarOpen.bind(this); } onSetSidebarOpen(open) { this.setState({ sidebarOpen: open }); } render() { return ( <Sidebar sidebar={<b>Sidebar content</b>} open={this.state.sidebarOpen} onSetOpen={this.onSetSidebarOpen} styles={{ sidebar: { background: "white" } }} > <button onClick={() => this.onSetSidebarOpen(true)}> Open sidebar </button> </Sidebar> ); } } export default App;Responsive sidebar
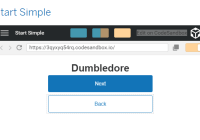
A common use case for a sidebar is to show it automatically when there is enough screen width available. This can be achieved using media queries via window.matchMedia. This again has to be integrated into the parent component so you can use the information to make changes to the sidebar and main content.
import React from "react"; import Sidebar from "react-sidebar"; const mql = window.matchMedia(`(min-width: 800px)`); class App extends React.Component { constructor(props) { super(props); this.state = { sidebarDocked: mql.matches, sidebarOpen: false }; this.mediaQueryChanged = this.mediaQueryChanged.bind(this); this.onSetSidebarOpen = this.onSetSidebarOpen.bind(this); } componentWillMount() { mql.addListener(this.mediaQueryChanged); } componentWillUnmount() { mql.removeListener(this.mediaQueryChanged); } onSetSidebarOpen(open) { this.setState({ sidebarOpen: open }); } mediaQueryChanged() { this.setState({ sidebarDocked: mql.matches, sidebarOpen: false }); } render() { return ( <Sidebar sidebar={<b>Sidebar content</b>} open={this.state.sidebarOpen} docked={this.state.sidebarDocked} onSetOpen={this.onSetSidebarOpen} > <b>Main content</b> </Sidebar> ); } } export default App;Supported props
| Property name | Type | Default | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| children | Anything React can render | n/a | The main content |
| rootClassName | string | n/a | Add a custom class to the root component |
| sidebarClassName | string | n/a | Add a custom class to the sidebar |
| contentClassName | string | n/a | Add a custom class to the content |
| overlayClassName | string | n/a | Add a custom class to the overlay |
| defaultSidebarWidth | number | 0 | Width in pixles of the sidebar on render. Use this to stop the sidebar from poping in after intial render. (Overrides transitions) |
| sidebar | Anything React can render | n/a | The sidebar content |
| onSetOpen | function | n/a | Callback called when the sidebar wants to change the open prop. Happens after sliding the sidebar and when the overlay is clicked when the sidebar is open. |
| docked | boolean | false | If the sidebar should be always visible |
| open | boolean | false | If the sidebar should be open |
| transitions | boolean | true | If transitions should be enabled |
| touch | boolean | true | If touch gestures should be enabled |
| touchHandleWidth | number | 20 | Width in pixels you can start dragging from the edge when the sidebar is closed. |
| dragToggleDistance | number | 30 | Distance the sidebar has to be dragged before it will open/close after it is released. |
| pullRight | boolean | false | Place the sidebar on the right |
| shadow | boolean | true | Enable/Disable sidebar shadow |
| styles | object | See below | Inline styles. These styles are merged with the defaults and applied to the respective elements. |
| rootId | string | n/a | Add an id to the root component |
| sidebarId | string | n/a | Add an id to the sidebar |
| contentId | string | n/a | Add an id to the content. The driving use case for adding an element id to content was to allow react-scroll to scroll the content area of the site using react-sidebar. |
| overlayId | string | n/a | Add an an id to the overlay |
Styles
Styles are passed as an object with 5 keys, root, sidebar, content, overlay and dragHandle, and merged to the following defaults:
{ root: { position: "absolute", top: 0, left: 0, right: 0, bottom: 0, overflow: "hidden" }, sidebar: { zIndex: 2, position: "absolute", top: 0, bottom: 0, transition: "transform .3s ease-out", WebkitTransition: "-webkit-transform .3s ease-out", willChange: "transform", overflowY: "auto" }, content: { position: "absolute", top: 0, left: 0, right: 0, bottom: 0, overflowY: "auto", WebkitOverflowScrolling: "touch", transition: "left .3s ease-out, right .3s ease-out" }, overlay: { zIndex: 1, position: "fixed", top: 0, left: 0, right: 0, bottom: 0, opacity: 0, visibility: "hidden", transition: "opacity .3s ease-out, visibility .3s ease-out", backgroundColor: "rgba(0,0,0,.3)" }, dragHandle: { zIndex: 1, position: "fixed", top: 0, bottom: 0 } };Acknowledgements
My goal was to make a React Component that implements the material design spec for navigation drawers. My initial attempt was to improve hamburger-basement by arnemart but I quickly figured that I better start from scratch. Still, that project helped me a ton to get started.