react-form-with-constraints
Simple form validation for React
- Installation:
npm install react-form-with-constraints - CDN: https://unpkg.com/react-form-with-constraints/dist/
Check the changelog for breaking changes and fixes between releases.
Introduction: what is HTML5 form validation?
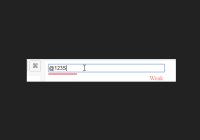
<form> <label for="email">Email:</label> <input type="email" id="email" required> <button>Submit</button> </form>The required HTML5 attribute specifies that the user must fill in a value, type="email" checks that the entered text looks like an email address.
Resources:
- Making Forms Fabulous with HTML5
- Constraint Validation: Native Client Side Validation for Web Forms
- MDN - Form data validation
- MDN - Form input types
- UX Research Articles - Usability Testing of Inline Form Validation
What react-form-with-constraints brings
- Minimal API and footprint
- Unobtrusive: easy to adapt regular React code
- HTML5 error messages personalization:
<FieldFeedback when="valueMissing">My custom error message</FieldFeedback> - Custom constraints:
<FieldFeedback when={value => ...}> - Warnings and infos:
<FieldFeedback ... warning>,<FieldFeedback ... info> - Async validation
- No dependency beside React (no Redux, MobX...)
- Re-render only what's necessary
- Easily extendable
- Bootstrap 4 styling with npm package
react-form-with-constraints-bootstrap4 - Material-UI integration with npm package
react-form-with-constraints-material-ui - Support for React Native with npm package
react-form-with-constraints-native - ...
<input type="password" name="password" value={this.state.password} onChange={this.handleChange} required pattern=".{5,}" /> <FieldFeedbacks for="password"> <FieldFeedback when="valueMissing" /> <FieldFeedback when="patternMismatch"> Should be at least 5 characters long </FieldFeedback> <FieldFeedback when={value => !/\d/.test(value)} warning> Should contain numbers </FieldFeedback> <FieldFeedback when={value => !/[a-z]/.test(value)} warning> Should contain small letters </FieldFeedback> <FieldFeedback when={value => !/[A-Z]/.test(value)} warning> Should contain capital letters </FieldFeedback> </FieldFeedbacks>Examples
-
CodePen basic Password example: https://codepen.io/tkrotoff/pen/BRGdqL (CodeSandbox version)
-
React Native example (React classes):
iOS Android 

-
Other examples from the examples directory:
How it works
The API works the same way as React Router:
<Router> <Route exact path="/" component={Home} /> <Route path="/news" component={NewsFeed} /> </Router>It is also inspired by AngularJS ngMessages.
If you had to implement validation yourself, you would end up with a global object that tracks errors for each field. react-form-with-constraints works similarly. It uses React context to share the FieldsStore object across FieldFeedbacks and FieldFeedback.
API
The API reads like this: "for field when constraint violation display feedback", example:
<FieldFeedbacks for="password"> <FieldFeedback when="valueMissing" /> <FieldFeedback when="patternMismatch">Should be at least 5 characters long</FieldFeedback> </FieldFeedbacks>for field "password" when constraint violation "valueMissing" display <the HTML5 error message (*)> when constraint violation "patternMismatch" display "Should be at least 5 characters long" Async support works as follow:
<FieldFeedbacks for="username"> <Async promise={checkUsernameAvailability} /* Function that returns a promise */ then={available => available ? <FieldFeedback key="1" info style={{color: 'green'}}>Username available</FieldFeedback> : <FieldFeedback key="2">Username already taken, choose another</FieldFeedback> // Why key=*? Needed otherwise React gets buggy when the user rapidly changes the field } /> </FieldFeedbacks>Trigger validation:
function MyForm() { const form = useRef(null); async function handleChange(e) { const target = e.target; // Validates only the given fields and returns Promise<Field[]> await form.current.validateFields(target); } async function handleSubmit(e) { e.preventDefault(); // Validates the non-dirty fields and returns Promise<Field[]> await form.current.validateForm(); if (form.current.isValid()) console.log('The form is valid'); else console.log('The form is invalid'); } return ( <FormWithConstraints ref={form} onSubmit={handleSubmit} noValidate> <input name="username" onChange={handleChange} required minLength={3} /> <FieldFeedbacks for="username"> <FieldFeedback when="tooShort">Too short</FieldFeedback> <Async promise={checkUsernameAvailability} then={available => available ? <FieldFeedback key="1" info style={{color: 'green'}}>Username available</FieldFeedback> : <FieldFeedback key="2">Username already taken, choose another</FieldFeedback> } /> <FieldFeedback when="*" /> </FieldFeedbacks> </FormWithConstraints> ); }Important note:
If a field (i.e an <input>) does not have a matching FieldFeedbacks, the library won't known about this field (and thus won't perform validation). The field name should match FieldFeedbacks.for:
<input name="MY_FIELD" ...> <FieldFeedbacks for="MY_FIELD"> ... </FieldFeedbacks>-
for: string=> reference to anameattribute (e.g<input name="username">), should be unique to the current formstop?: 'first' | 'first-error' | 'first-warning' | 'first-info' | 'no'=> when to stop renderingFieldFeedbacks, by default stops at the first error encountered (FieldFeedbacks order matters)
Note: you can place
FieldFeedbacksanywhere, have as many as you want for the samefield, nest them, mix them withFieldFeedback... Example:<input name="username" ... /> <FieldFeedbacks for="username" stop="first-warning"> <FieldFeedbacks> <FieldFeedback ... /> <Async ... /> <FieldFeedbacks stop="first-info"> ... </FieldFeedbacks> </FieldFeedbacks> <FieldFeedback ... /> <Async ... /> </FieldFeedbacks> <FieldFeedbacks for="username" stop="no"> ... </FieldFeedbacks>
-
when?:ValidityStateas a string => HTML5 constraint violation name'*'=> matches any HTML5 constraint violation'valid'=> displays the feedback only if the field is valid(value: string) => boolean=> custom constraint
error?: boolean=> treats the feedback as an error (default)warning?: boolean=> treats the feedback as a warninginfo?: boolean=> treats the feedback as an infochildren=> what to display when the constraint matches; if missing, displays the HTML5 error message if any
-
Async<T>=> Async version ofFieldFeedback(similar API as react-promise)promise: (value: string) => Promise<T>=> a promise you want to wait forpending?: React.ReactNode=> runs when promise is pendingthen?: (value: T) => React.ReactNode=> runs when promise is resolvedcatch?: (reason: any) => React.ReactNode=> runs when promise is rejected
-
-
validateFields(...inputsOrNames: Array<Input | string>): Promise<Field[]>=> Should be called when afieldchanges, will re-render the properFieldFeedbacks (and update the internalFieldsStore). Without arguments, all fields ($('[name]')) are validated. -
validateFieldsWithoutFeedback(...inputsOrNames: Array<Input | string>): Promise<Field[]>=> Validates only all non-dirty fields (won't re-validate fields that have been already validated withvalidateFields()), If you want to force re-validate all fields, usevalidateFields(). Might be renamed tovalidateNonDirtyFieldsOnly()orvalidateFieldsNotDirtyOnly()in the future? -
validateForm(): Promise<Field[]>=> Same asvalidateFieldsWithoutFeedback()without arguments, typically called before to submit theform. Might be removed in the future? -
isValid(): boolean=> should be called aftervalidateFields(),validateFieldsWithoutFeedback()orvalidateForm(), indicates if the fields are valid -
hasFeedbacks(): boolean=> indicates if any of the fields have any kind of feedback -
resetFields(...inputsOrNames: Array<Input | string>): Promise<Field[]>=> Resets the given fields and re-render the properFieldFeedbacks. Without arguments, all fields ($('[name]')) are reset. -
Field=>{ name: string; validations: { // FieldFeedbackValidation[] key: number; type: 'error' | 'warning' | 'info' | 'whenValid'; show: boolean | undefined; }[]; isValid: () => boolean }
-
-
If you want to style
<input>, use<Input>instead: it will add classesis-pending,has-errors,has-warnings,has-infosand/oris-validon<input>when the field is validated.Example:
<Input name="username" />can generate<input name="username" class="has-errors has-warnings">FYI
react-form-with-constraints-bootstrap4andreact-form-with-constraints-material-uialready style the fields to match their respective frameworks.
Browser support
react-form-with-constraints needs ValidityState which is supported by all modern browsers and IE >= 10. It also needs a polyfill such as core-js to support IE >= 10, see React JavaScript Environment Requirements.
You can use HTML5 attributes like type="email", required, minlength...
<label htmlFor="email">Email</label> <input type="email" name="email" id="email" value={this.state.email} onChange={this.handleChange} required /> <FieldFeedbacks for="email"> <FieldFeedback when="*" /> </FieldFeedbacks>...and/or rely on when functions:
<label htmlFor="email">Email</label> <input name="email" id="email" value={this.state.email} onChange={this.handleChange} /> <FieldFeedbacks for="email"> <FieldFeedback when={value => value.length === 0}>Please fill out this field.</FieldFeedback> <FieldFeedback when={value => !/\S+@\S+/.test(value)}>Invalid email address.</FieldFeedback> </FieldFeedbacks>In the last case you will have to manage translations yourself (see SignUp example).
How to consume the npm packages?
ESNext (currently ES2018) + ES modules
Files inside lib/ (package.json "module": "lib/index.js").
A recent browser or Node.js is required or you will need to transpile the react-form-with-constraints source code using Babel (or TypeScript tsc).
Several advantages:
- The combine use of
"sideEffects": falsewith"module": ...generates a smaller bundle thanks to tree shaking - You can transpile react-form-with-constraints source code with your Babel's preset-env and Browserslist configuration
For this to work, do not exclude node_modules from your webpack configuration, example:
// webpack.config.js module: { rules: [ { test: /\.(js|jsx?)$/, // See [Enable babel-preset-env for node_modules that target newer Node versions](https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app/issues/1125) // See [Create React App 2.0: "You can now use packages written for latest Node versions without breaking the build"](https://reactjs.org/blog/2018/10/01/create-react-app-v2.html) // See ["If you have to exclude node_modules/, how do you get babel to polyfill/transform code in 3rd party code?"](https://github.com/webpack/webpack/issues/6544#issuecomment-417108242) // See [Compile dependencies with babel-preset-env](https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app/pull/3776) //exclude: /node_modules/, exclude: /\/core-js/, loader: 'babel-loader', options: { // See https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app/blob/v2.1.0/packages/react-scripts/config/webpack.config.dev.js#L284 compact: false } } ] }You probably want to configure Babel with sourceType: 'unambiguous':
// babel.config.js module.exports = { // See https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app/blob/v2.1.0/packages/babel-preset-react-app/dependencies.js#L64 // See [Add Babel config sourceType: 'unambiguous' for dependencies](https://github.com/facebook/create-react-app/pull/5052) sourceType: 'unambiguous', presets: [ [ '@babel/preset-env', { useBuiltIns: 'usage', corejs: 3 } ], '@babel/preset-react' ], plugins: [ '@babel/plugin-proposal-class-properties', '@babel/plugin-proposal-object-rest-spread' ] };ES5 + CommonJS
Classic ES5 transpilation, files inside lib-es5/ (package.json "main": "lib-es5/index.js"). No tree shaking.
UMD (Universal Module Definition) + ES5
Files inside dist/. Typical use is with <script src="react-form-with-constraints.production.min.js"> inside your index.html.
A good use case is CodePen, files are generated by Rollup.
Notes
- A
type="hidden",readonlyordisabledinput won't trigger any HTML5 form constraint validation likerequired, see https://codepen.io/tkrotoff/pen/gdjVNv