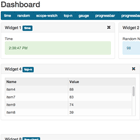
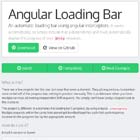
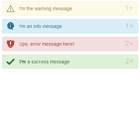
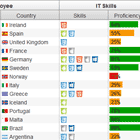
angular-dashboard

Generic AngularJS component/directive providing dashboard/widgets functionality.
Features:
-
Adding/removing widgets
-
Widgets are instantiated dynamically (from corresponding directive or template)
-
Widgets drag and drop (with jQuery UI Sortable)
-
Horizontal and vertical widgets resize
-
Fluid layout (widgets can have percentage-based width, or have width set in any other unit)
-
Any directive or template can be a widget
-
Connecting widgets to real-time data (WebSocket, REST, etc.)
-
Changing widget data source dynamically (from widget options)
-
Saving widgets state to local storage
-
Multiple Dashboard Layouts
Contributing
This project welcomes new contributors.
You acknowledge that your submissions to DataTorrent on this repository are made pursuant the terms of the Apache License, Version 2.0 (http://www.apache.org/licenses/LICENSE-2.0.html) and constitute "Contributions," as defined therein, and you represent and warrant that you have the right and authority to do so.
When adding new javascript files, please prepend the Apache v2.0 license header, which can be found in CONTRIBUTING.md file.
Examples
Simple demo (minimum dependencies) [source code]
Advanced demo (charts, visualization, data sources, etc.) [source code]
UI Console (very complex application; REST, WebSocket and Socket.IO data sources; dashboard customization; etc.) [source code]
Widget Library using the dashboard [source code]
Build
Project is built with Gulp.
$ npm install -g gulp $ gulpRequirements
- AngularJS
- Underscore.js
- jQuery
- jQuery UI
- Angular UI Sortable
- Angular Bootstrap
Example of including dependencies from CDN here
Getting Started
See demo (several widgets) for a quick start.
Running demo.
$ bower install $ gulp build:demo $ gulp serveApplication will be available at http://localhost:3000/
download
With bower:
bower install malhar-angular-dashboard For legacy reasons, this bower module is also registered as angular-ui-dashboard.
Manually:
Download the zip of this repo and use the files in the dist folder.
include
Load dist/malhar-angular-dashboard.js and dist/malhar-angular-dashboard.css in your html:
<link rel="stylesheet" href="bower_components/malhar-angular-dashboard/dist/malhar-angular-dashboard.css"> <script src="bower_components/malhar-angular-dashboard/dist/malhar-angular-dashboard.js"></script>Also be sure to add it to your apps dependency list:
angular.module('yourApp', [ // other dependencies 'ui.dashboard' ]);Controller Scope vs. DataModel
Widgets inherit controller scope (so normally different widgets will have bindings to different controller scope properties).
DataModel has direct access to widget scope, each widget has separate instance of DataModel.
Usage
Include the dashboard directive on the element you wish to place widgets in:
<div dashboard="dashboardOptions"></div>Custom Template
It is possible to use your own template for the dashboard and widget markup (replacing dashboard/dashboard.html). To do so, include a template-url attribute on the element to become dashboard:
<div dashboard="dashboardOptions" template-url="path/to/my-template.html"></div>dashboardOptions
dashboardOptions in the above html is required and should be an object available on the current scope. The options on said object are as follows:
| key | type | default value | required | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| widgetDefinitions | Array | n/a | yes | List of Widget Definition Objects. See below for available options on those. |
| defaultWidgets | Array | n/a | yes | List of objects where an object is { name: [NAME_OF_WIDGET_DEFINITION] }. TODO: Allow just list of names. |
| widgetButtons | Boolean | true | no | Display buttons for adding and removing widgets. |
| storage | Object | null | no | If defined, this object should implement three methods: setItem, getItem, and removeItem. See the Persistence section below. |
| storageId | String | null | no (yes if storage is defined) | This is used as the first parameter passed to the three storage methods above. See the Persistence section below. |
| storageHash | String | '' | no | This is used to validate/invalidate loaded state. See the Persistence section below. |
| stringifyStorage | Boolean | true | no | If set to true, the dashboard state will be converted to a JSON string before being passed to storage.setItem. Likewise, it will be passed through JSON.parse after being retrieved from storage.getItem. See the Persistence section below. |
| explicitSave | Boolean | false | no | The dashboard will not automatically save to storage for every change. Saves must instead be called explicitly using the saveDashboard method that is attached to the option event upon initialization. |
| sortableOptions | Object | n/a | no | Allows to specify the various sortable options of the underlying jQuery UI Sortable. |
| hideWidgetSettings | Boolean | false | no | If true, the cog button in the top right corner of each widget will not be present. |
| hideWidgetClose | Boolean | false | no | If true, the "x" button in the top right corner of each widget will not be present. |
| settingsModalOptions | Object | see below | no | The options object to be passed to the $uibModal service for widget settings. See the Custom Widget Settings section below. |
| onSettingsClose | Function | see below | no | The success callback for when a widget settings dialog is closed by the user. See the Custom Widget Settings section below. |
| onSettingsDismiss | Function | see below | no | The error callback for when a widget settings dialog is dismissed by the user. See the Custom Widget Settings section below. |
Upon instantiation, this options object is endowed with a few API methods for use by outside code: addWidget, loadWidgets, saveDashboard and loadDashboard.
Widget Definition Objects
You can think of Widget Definition Objects as a class and the widgets on the page as instances of those classes. The options for a Widget Definition Object are:
| key | type | default value | required | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| name | String | n/a | true | Name of Widget Definition Object. If no templateUrl, template, or directive are on the Widget Definition Object, this is assumed to be a directive name. In other words, the directive attribute is set to this value. |
| title | String | n/a | false | Default title of widget instances |
| attrs | Object | n/a | false | Map of attributes to add to the markup of the widget. Changes to these will be stored when using the storage option |
| templateUrl | String | n/a | false | URL of template to use for widget content |
| template | String | n/a | false | String template (ignored if templateUrl is present) |
| directive | String | n/a | false | HTML-injectable directive name (eg. "ng-show") |
| dataModelType | Function or String | n/a | false | Constructor for the dataModel object, which provides data to the widget (see below for more information). |
| dataModelOptions | Object | n/a | false | Arbitrary values to supply to the dataModel. Available on dataModel instance as this.dataModelOptions. Serializable values in this object will also be saved if storage is being used (see the Persistence section below). |
| dataModelArgs | Object | n/a | false | Object to be passed to data model constructor function. This object is not serialized by default and if defined should be present in widget definitions. |
| dataAttrName | String | n/a | false | Name of attribute to bind widgetData model |
| storageHash | String | n/a | false | This is analogous to the storageHash option on the dashboard, except at a widget-level instead of a dashboard-wide level. This can be helpful if you would only like to invalidate stored state of one widget at a time instead of all widgets. |
| settingsModalOptions | Object | see below | no | Overrides same-named option in dashboard options for this widget. See the Custom Widget Settings section below. |
| size | Object | n/a | false | Widget size, e.g { width: '50%', minWidth: '27%', height: '250px' } |
| style | Object | n/a | false | Widget style, e.g { float: 'right' } |
| enableVerticalResize | Boolean | true | false | Option to enable/disable vertical resize. Should be provided in "widgetDefinitions" since it is not serialized by default. |
| onSettingsClose | Function | see below | no | Overrides same-named option in dashboard options for this widget. See the Custom Widget Settings section below. |
| onSettingsDismiss | Function | see below | no | Overrides same-named option in dashboard options for this widget. See the Custom Widget Settings section below. |
| serialize | Function | see below | no | Define this to override how this widget gets saved to storage. See persistence section below. |
As of v1.0.0, you can also add arbitrary data to your WDOs and this data will be copied to your widget. Keep in mind though, that if you want to SAVE some of this arbitrary info with storage, you will need to implement your own serialize method that includes this (see the persistence section below).
Widget Resize
Widgets width and height is controlled with size attribute (serialized by default). Width can be both unit and percentage based.
Example
{ name: 'fluid', directive: 'wt-fluid', size: { width: '50%', minWidth: '27%', height: '250px' } }Widgets can be resized both horizontally and vertically and size is serialized.
When widget is resized 'widgetResized' event is broadcasted to the widget scope.
dataModelType
The best way to provide data to a widget is to specify a dataModelType in the Widget Definition Object (above). This function is used as a constructor whenever a new widget is instantiated on the page. If dataModelType is a string it will be looked up with $injector (it should be valid AngularJS provider/factory/service). In most cases data model should implement the following methods: init, and destroy. Please see widget directive file for implementation details.
setup
This function is called once when a widget is instantiated. It takes two arguments: (1) the instance of the WidgetModel constructor that corresponds to the widget instance, and (2) the scope of the widget.
init
This function is called once when a widget is instantiated. This function does not take any arguments.
destroy
This function is called when the widget is removed from the dashboard. It does not take any arguments. It should be used to clean up any listeners that may otherwise hang around, e.g. unsubscribing to a WebSocket topic or RESTful endpoint.
It is recommended to prototypically extend from the WidgetDataModel constructor, which implements the setup function. Take a look at the code here.
Here is an example way to extend from WidgetDataModel:
angular.module('myApp') // Inject other services like $http here, if necessary: .factory('MyDataModel', ['WidgetDataModel', function (WidgetDataModel) { function MyDataModel() {} MyDataModel.prototype = Object.create(WidgetDataModel.prototype); MyDataModel.prototype.init = function() { // My custom data model setup, like subscribing // to WebSocket or starting a REST call interval } MyDataModel.prototype.destroy = function() { // My custom data model teardown, like unsubscribing // to WebSocket or clearing a setInterval } return MyDataModel; }]);Persistence
This dashboard component offers a means to save the state of the user's dashboard. Specifically, the dashboard can automatically save:
- instantiated widgets
- size of widgets (width and height)
- order that widgets are displayed
- widget titles
- any serializable data stored in
dataModelOptionsif the widget instance has ads(instantiateddataModelType)
There are four options you can specify in the dashboardOptions object relating to persistence:
storage (Object)
This object will be used by the dashboard to save its state. It should implement the following three methods:
- storage.getItem(String
key) This method will be used to attempt to retrieve previous dashboard state. It can return either a string or a promise. "promise" in this context simply means an object that has athenfunction that takes asuccessCallbackanderrorCallbackas its first and second arguments. This follows the most common promise interface (it works with angular's$qpromise, jQuery's$.Deferred()promise, and many others). - storage.setItem(String
key, Stringvalue) This method is assumed to storevaluein a way that will be accessible later via thegetItemmethod above. - storage.removeItem(String
key) This method is assumed to remove items set with thesetItemmethod above.
storageId (String)
This string will be used as the key argument in the three methods on the storage object, outlined above. This allows for multiple dashboard instances to exist with storage on a single page and site. This is required in order for storage to work.
storageHash (String)
This string will be stored along with the dashboard state. Then later, when state is loaded, the loaded value will be compared to the value passed to dashboardOptions. If the values are different, the item in storage will be assumed to be invalid and removeItem will be called to clear it out. This is so that if you as the developer makes changes that are not backwards compatible with previous dashboard configurations, you can simply change the storageHash and not have to worry about strange behavior due to stale dashboard state. This is optional but is highly recommended.
stringifyStorage (Boolean)
By default (stringifyStorage=true), the dashboard will convert its state (a JavaScript Object) to a string using JSON.stringify before passing it to storage.setItem. Additionally, the dashboard will assume that storage.getItem will return a JSON string and try to parse it with JSON.parse. This works with window.localStorage nicely, since objects cannot be used as value in localStorage.setItem(key, value). However, if you are implementing your own storage and would not like this stringification business, set stringifyStorage to false.
There are also two options you can specify on WDOs that relate to persistence:
storageHash (String)
Analogous to the storageHash option on the dashboard, except at a widget-level instead of a dashboard-wide level. This can be helpful if you would only like to invalidate stored state of one widget at a time instead of all widgets.
serialize (Function)
This function will determine how the state of the widget gets saved. It takes no arguments and should return a JSON.stringifyable object. The default implementation is as follows:
serialize: function() { return _.pick(this, ['title', 'name', 'style', 'size', 'dataModelOptions', 'attrs', 'storageHash']); }See _.pick for more details. The most common use-case for this would be to add another key to this list, or remove a key.
Custom Widget Settings
Unless the hideWidgetSettings option is set to true on the dashboard options, each widget by default has a "cog" button in the top right corner that, when clicked, opens up a "modal" (dialog box) with information about the widget and controls to change the title. As of this writing, the default functionality is very minimal; only the widget's title can be changed from this modal. In many cases, you will want to replace and extend the default functionality. In rarer cases, you may even want to override the functionality for a specific widget class. Both of these use-cases are possible using this module.
Principles
To understand how these overrides work, it is beneficial to understand what's happening behind the scenes (if you are looking in the code, the relevant snippet is located in src/directives/dashboard.js, in the method openWidgetSettings). The widget settings modal uses a service called $uibModal from the angular-bootstrap project. Specifically, the dashboard calls $uibModal.open(options) where options is an object containing (ehem) options for the $uibModal service to use. The relevant options for understanding widget settings are:
templateUrl: Should point to the template to be used to build the modal markup. The default in this dashboard istemplate/widget-settings-template.html.controller: A string that points to a registered angular controller. This controller handles the behaviors in the modal. The default in this dashboard isWidgetSettingsCtrl, located atsrc/controllers/widgetSettingsCtrl.js.resolve: An object where key is an injectable name and value is a function that returns the injected value in the controller. In the case of this dashboard, this property is always set to resolve the widget model so it can be injected into the$uibModalcontroller.
For a full list of options, visit the angular-bootstrap website and scroll to the $uibModal service section.
When the user is done viewing the modal, it is either dismissed (the user presses "cancel", meaning he wants to discard any changes made) or it is closed (the user presses "ok", meaning he wants to save his changes). These two outcomes are handled by a $uibModalInstance promise that is either resolved or rejected (for information on promises, see the angular documentation).
Overriding Widget Settings for Every Widget
To override the options object that gets passed to $uibModal.open(options) for all widgets (i.e. you want to provide a different default templateUrl and/or controller for all widget settings), you may assign an options object to the settingsModalOptions key in your dashboard options:
// ... in your controller $scope.myDashboardOptions = { widgetDefinitions: myWidgetDefinitions, defaultWidgets: myDefaultWidgets, settingsModalOptions: { templateUrl: 'my/custom/widgetSettingsTemplate.html', controller: 'MyCustomWidgetSettingsCtrl' // defined elsewhere, // other $uibModal.open options can go here, eg: // backdrop: false, // keyboard: false } }; NOTE: The resolve object gets provided to the $uibModal options by the dashboard, and contains only the widget instance as widget. If you put resolve in settingsModalOptions it will be ignored.
To override the callbacks that get passed to the $uibModalInstance promise, assign functions to the onSettingsClose and onSettingsDismiss keys on your dashboard options:
// ... in your controller $scope.myDashboardOptions = { widgetDefinitions: myWidgetDefinitions, defaultWidgets: myDefaultWidgets, settingsModalOptions: { templateUrl: 'my/custom/widgetSettingsTemplate.html', controller: 'MyCustomWidgetSettingsCtrl' }, onSettingsClose: function(resultFromModal, widgetModel, dashboardScope) { // do something to update widgetModel, like the default implementation: jQuery.extend(true, widget, result); }, onSettingsDismiss: function(reasonForDismissal, dashboardScope) { // probably do nothing here, since the user pressed cancel } }; Overriding Widget Settings for a Specific Widget Definition
Overriding widget settings for a specific widget is almost exactly like overriding the default for the entire dashboard, except that you place settingsModalOptions, onSettingsClose, and onSettingsDismiss onto the Widget Definition Object itself:
// ... in your controller $scope.myDashboardOptions = { widgetDefinitions: [ { name: 'myAwesomeWidget', template: '<div>hello {{widget.title}}</div>', settingsModalOptions: { templateUrl: 'my/custom/widgetSettingsTemplate.html', controller: 'MyCustomWidgetSettingsCtrl' }, onSettingsClose: function(resultFromModal, widgetModel, dashboardScope) { // do something to update widgetModel, like the default implementation: jQuery.extend(true, widget, result); }, onSettingsDismiss: function(reasonForDismissal, dashboardScope) { // probably do nothing here, since the user pressed cancel } } ], defaultWidgets: myDefaultWidgets }; Dashboard Layouts
One common requirement for user-customizable dashboards is the ability to have multiple layouts consisting of the same set of widget definitions. This sounds more confusing than it is, so the best way to understand it is to take a look at the layouts demo. You can also see this demo by running gulp serve and navigating to /#/layouts (or /#/layouts/explicit-saving, behavior when options.explicitSave is true). This is achieved by using the dashboard-layouts directive:
<div dashboard-layouts="layoutOptions"></div>layoutOptions
The layoutOptions object passed to dashboard-layouts tries to mirror dashboardOptions as closely as possible:
| key | type | default value | required | description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| widgetDefinitions | Array | n/a | yes | Same as in dashboardOptions |
| lockDefaultLayouts | Boolean | false | no | true to lock default layouts (prevent from removing and renaming), layout lock can also be controlled with locked layout property |
| defaultLayouts | Array | n/a | yes | List of objects where an object is { title: [STRING_LAYOUT_TITLE], active: [BOOLEAN_ACTIVE_STATE], locked: [BOOLEAN], defaultWidgets: [ARRAY_DEFAULT_WIDGETS], widgetDefinitions: [ARRAY_OF_WIDGET_DEFS] }. Note that defaultWidgets is the same as in dashboardOptions. Also note that the widgetDefinitions array is optional on individual default layouts. By default, layouts will use the widgetDefintions from the dashboardLayouts options object. See issue #83. |
| widgetButtons | Boolean | true | no | Same as in dashboardOptions |
| storage | Object | null | no | Same as in dashboardOptions, only the saved objects look like: { layouts: [...], states: {...}, storageHash: '' } |
| storageId | String | null | no (yes if storage is defined) | This is used as the first parameter passed to the three storage methods setItem, getItem, removeItem. See the Persistence section above. |
| storageHash | String | '' | no | Same as in dashboardOptions |
| stringifyStorage | Boolean | true | no | Same as in dashboardOptions |
| explicitSave | Boolean | false | no | Same as in dashboardOptions |
| sortableOptions | Object | n/a | no | Same as in 'dashboardOptions' |
As with dashboardOptions, layoutOptions gets endowed with the methods addWidget, loadWidgets, saveDashboard and loadDashboard. These will be applied to the currently active dashboard layout. Additionally, a method called saveLayouts is attached to the layoutOptions object. This method will save the state of the layouts explicitly.
Links
malhar-angular-widgets Widget library (widgets, data models, WebSocket, etc.)
malhar-dashboard-webapp Demo using this dashboard and widget library
Node.js Software platform built on JavaScript runtime
AngularJS JavaScript framework
ui-sortable AngularJS UI Sortable
jQuery UI Sortable jQuery UI Sortable plugin (reordering with drag and drop)
Bower Package manager for the web
Grunt JavaScript task runner
Gulp Streaming build system