Vue Smooth Reflow (VSR)
A Vue mixin that transitions reflow.
When the component's data is changed, any CSS properties that you register will transition to its new value.
Common use cases are:
- Transitioning
height: autoandwidth: auto. - Smoothly repositioning elements.
Note that this library has no overlap with Vue's built in <transition> components.
Table of Contents
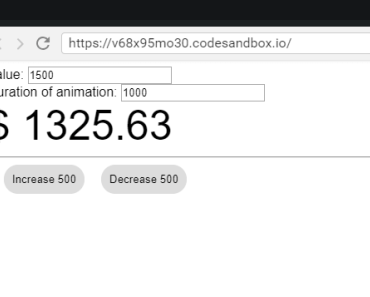
Demo
https://vuesmoothreflow.guanzo.io
If you want to see how the examples were configured, the demo source is here: github
Installation
Download via npm:
$ npm install vue-smooth-reflowInclude via cdn:
<script src="https://unpkg.com/vue-smooth-reflow"></script>Usage
Module:
<template> <div> <div v-for="n in children" /> </div> </template> <script> // The component's root el will now transition to // accomodate new values of 'this.children' import smoothReflow from 'vue-smooth-reflow' export default { mixins: [smoothReflow], data() { return { children: '<Dynamic value>' } }, mounted(){ this.$smoothReflow() }, } </script>Browser:
The mixin is available via the global variable SmoothReflow
API
$smoothReflow(options)
Enables smooth reflow on an element. This method is available on the component instance.
options can be an object, or an array of objects.
Options reference
-
elType:
Element | StringDefault: The components root element.
An element reference, or a CSS selector string. The resolved element will transition reflows on registered properties. This element is referred to as the "smooth element".
Use a selector string if the element is not rendered initially, like if it's hidden with
v-if. If the selector returns multiple elements, the first one will be used. -
propertyType:
String | ArrayDefault:
heightValid values:
height,width,transformThe CSS property(s) that you want to transition. You can pass any combination.
For
transform, VSR will only transition thetranslate()function. This is to handle element repositioning due to reflow. -
transitionType:
StringDefault:
height .5sA valid CSS transition value. If you register multiple properties, and want different transitions for each, you can use commas.
this.$smoothReflow({ property: ['height', 'width'], transition: 'height .25s ease-in-out, width .75s ease-out' })
The default value is conditional on the
propertyoption.For example, if you register
heightandtransformlike so:this.$smoothReflow({ property: ['height', 'transform'] })
The default value will become
height .5s, transform .5s.If the smooth element has transitions on other properties like
background-color, they will be preserved.NOTE: Any transitions defined as an inline style on the smooth element will be ignored and erased.
-
transitionEventType:
ObjectDefault:
nullValid values:
transitionEvent: { // Any valid CSS selector. Note that comma delimited selectors are valid. selector: String, // Any valid CSS property name. propertyName: String }
Configures the smooth element to react to
transitionendevents that are emitted by other elements. You must opt-in for this behavior, there is no default.selectorandpropertyNameserve as filters so that the smooth element doesn't cause reflows for everytransitionendevent that it catches, which impacts performance. When the smooth element receives atransitionendevent, it will check ifselectormatchesevent.target, and/or ifpropertyNamematchesevent.propertyName. You can specify one or the other, or both. All checks must pass in order for the smooth element to proceed with the smooth reflow.A common use case is to delay the smooth reflow until after a child element has been transitioned out with
v-if/v-showand<transition>.For example, if you want to react to any child
divelements that transition out with opacity, use this config:transitionEvent: { selector: 'div', propertyName: 'opacity' }
Let's say you want to transition the smooth element's position. You want to wait for an element with class
.i-cause-reflowto transition out before performing the smooth reflow. This element can be located anywhere within the component. Here's the configuration for that:transitionEvent: { selector: '.i-cause-reflow', }
Check out the demo for more examples.
-
hideOverflowType:
BooleanDefault:
trueHides overflow during the transition.
This has 2 benefits. It prevents the scrollbar from appearing, and will hide child elements that overflow.
$unsmoothReflow(options)
Disables smooth reflow on an element. This method is available on the component instance.
options can be an object, or an array of objects.
Registered elements that have the same el as the passed in options will be unregistered. This usually isn't necessary, but is useful if you want to disable the behavior while the component is still alive.
Smooth Component
Importing VSR into every component that needs it violates DRY. Instead, you can create one component that imports VSR then use it as needed. This should satisfy 90% of use cases.
Example:
// SmoothReflow.vue <template> <component :is="tag"> <slot/> </component> </template> <script> import smoothReflow from 'vue-smooth-reflow' export default { name: 'SmoothReflow', mixins: [smoothReflow], props: { tag: { type: String, default: 'div' }, options: Object, }, mounted () { this.$smoothReflow(this.options) } } </script> Globally register this component for convenience.
// main.js import SmoothReflow from './components/SmoothReflow' Vue.component('SmoothReflow', SmoothReflow)Update your existing components that import VSR. This is a modification of the first usage example. Goodbye boilerplate!
<template> <SmoothReflow> <div v-for="n in children"/> </SmoothReflow> </template> <script> -import smoothReflow from 'vue-smooth-reflow' export default { - mixins: [smoothReflow], data() { return { children: '<Dynamic value>' } }, - mounted(){ - this.$smoothReflow() - }, } </script>You may run into reactivity issues when using the SmoothComponent. VSR hooks into the component's beforeUpdate and updated lifecycle methods, so if those are never called, then the transition won't occur.
Examples:
mounted(){ // Zero config. Enables smooth reflow on this.$el this.$smoothReflow() // Register with element reference this.$smoothReflow({ el: this.$refs.wrapper, }) // Register with classname. The first match will be used. this.$smoothReflow({ el: '.wrapper-2', }) // Pass an array of options this.$smoothReflow([ // Wait for .reflow-causer to emit a transitionend event, // then transition the smooth element's position { el: this.$refs.wrapper, property: 'transform', transitionEvent: { selector: '.reflow-causer' } }, // Wait for a transitionend event for opacity that // comes from the smooth elements descendants, // then transition the smooth elements height and width. { el: '.wrapper-2', property: ['height', 'width'], transitionEvent: { propertyName: 'opacity' } }, ]) // If the element reference is a component, // make sure to pass in its "$el" property. this.$smoothReflow({ el: this.$refs.wrapper.$el, }) // Unregister a smooth element that would match // the selector '.wrapper-5' this.$unsmoothReflow({ el: '.wrapper-5' }) } </script> Differences from vue-smooth-height
-
Enables smooth reflows on
widthandtransform. -
VSR will no longer check for existing transition values for registered properties. It will only use the value of the
transitionoption. -
The
hideOverflowoption now defaults totrue. -
The way child transitions are handled is completely different.
License
Copyright (c) 2013-present, Eric Guan