DynModal v1.0.2
DynModal is a small application/plugin written in Typescript that dynamically creates Bootstrap 4 modals without the need to inject raw HTML into each page you wish for a modal to appear.
Table of Contents
- Requirements
- Getting Started
- Basic Examples
- Constructor Options
- Convenience Method(s)
- Bug/Feature Requests
- Contributing
- License
Requirements
Getting Started
- Download the latest version or compile from the source
- Require jQuery and Bootstrap (see above for links) in script tags
- Require DynModal in a script tag (after the aforementioned)
<script src="/path/to/dynmodal.min.js"></script>Basic Examples
Creating a DynModal instance
In the following basic examples, we will go over how to create a simple DynModal object instance, and configure it to show some content to the user visiting our website.
let dynmodal = new DynModal.Core();In this most basic example, we have created a new DynModal object with the default options set. If you wish to customize your options, please visit the options section for more information.
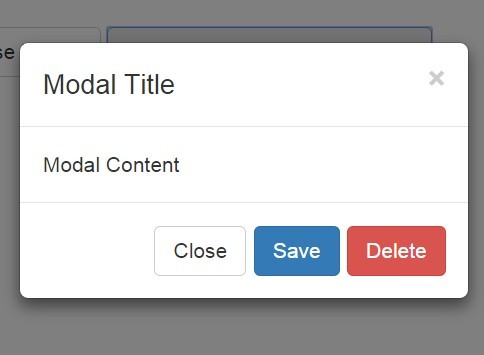
Building a modal
Now that we have created a DynModal instance, we can now create a new modal instance by building it. In order to build a modal, we will specify some options via the set...() functions and then invoke build() to complete the process.
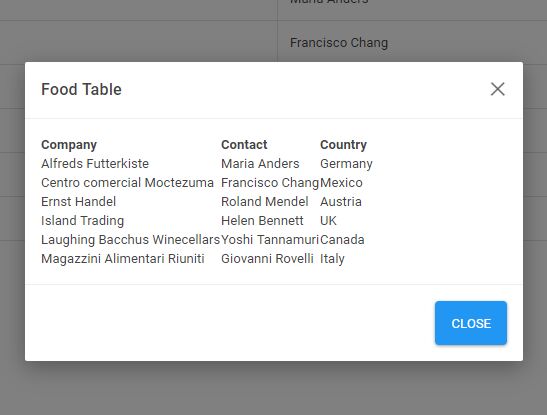
dynmodal.setHeaderTitle("Food Table") .setShowCloseButton(true) .setBody(() => $("#foodTable").html()) .buildAndShow();The functions above should be rather self-explanatory. Please make note of the setBody(function) method, however. Since we want to allow the developer to change the contents of the modal, here is where that would occur.
The setBody(function) function returns a callback inside the argument. This return MUST be a string. If it is not a string, an error will be thrown. Here are some examples of how the function may ben used to generate a modal body:
... // Return a raw HTML string .setBody(function() { return "<p>This is my modal content</p>"; }) ... // Return a string via raw JavaScript .setBody(function() { return document.getElementById("#foodTable").innerHTML; }) ... // Return a string via a jQuery object .setBody(function() { return $("body #foodTable").html(); }) ... // Return a jQuery object that will be cloned .setBody(function() { return $("#foodTable").clone(); }); ...Notice that the function only requires that a string containing HTML be passed back to it. It does not care how you obtain that information, so it is completely possible to generate it yourself, render it from an object on the page, or even load it via AJAX from an API server.
Building a footer
The footer of the modal almost always consist of a button or two. For this reason, DynModal has made it as easy as possible to implement your own footer buttons as necessary. To do so, invoke setFooter(Array<String>) before the modal has been built. The Array<String> portion is an array of raw HTML that, when parsed, will be shown to the user.
... .setFooter([ "<button type='button' class-'btn btn-primary'>Save Changes</button>", "<button type='button' class='btn btn-danger' data-close>Close</button>" ]) ...Notice that the array we are passing in is simply an array of HTML button elements. As such, when the HTML is parsed by DynModal, it will appear just as it was written in this function; however, there is once instance in which DynModal will replace your markup: data-close.
Since you may wish to retain or modify the close button, DynModal allows you to insert a data-close attribute within a button you wish to have used to close the modal. Each time a new modal is created, DynModal will update this attribute to reflect the most recent modal ID.
Showing the modal
Now that the modal has been modified to the developers likings and it has been built by invoking the build() function, you may now proceed to show the modal to the user. There are two ways to show the modal: show() and buildAndShow(). The former will require that you invoke build() separately before showing the modal, whereas the latter will allow you to both build and show the modal via one invocation.
Hiding the modal
Lastly, DynModal will retain basic Bootstrap 4 features, such as hiding the modal when the user clicks outside the viewport. However, if you wish to programmatically force the modal to hide itself, you make invoke the hide(force: boolean) function.
If you set the force attribute to true, then DynModal will forcefully call upon Bootstrap 4 to close the modal. If it set to false, however, DynModal will attempt to hide the modal, but no real effort will be made thereafter if the modal still appears on the user's screen.
Constructor Options
centerVertically
Description: Set to true if the modal should be vertically centered in the page
Type: boolean
Default: false
removeAnimation
Description: Set to true if the modal should appear without any fade animation
Type: boolean
Default: false
size
Description: Specify the size of the modal to show on the screen
Type: ModalSize
Default: ModalSize.DEFAULT
Values: [ModalSize.SMALL, ModalSize.DEFAULT, ModalSize.LARGE]
onBuilt
Description: Called when the modal has been built via the build() method
Type: function
Method Signature: onBuilt(core: DynModal.Core)
onShown
Description: Called when the modal has fully been shown to the user
Type: function
Method Signature: onShown(id: number, modal: jQuery<HTMLElement>)
onHidden
Description: Called when the modal has been hidden. This callback could be invoked via the user clicking outside of the viewport or the developer invoking the hide(force: boolean) method.
Type: function
Method Signature: onHidden(id: number)
Convenience Method(s)
fromTemplate
Description: Retrieves a jQuery object containing the contents of the DOM object with the specified selector (if that object is an HTML5 <template/> tag. If is not, an error will be thrown.
Type: static function
Method Signature: fromTemplate(selector: string): JQuery<HTMLElement>
let $template = DynModal.Core.fromTemplate("template#foodTemplate");Bug/Feature Requests
No piece of software is without bugs, and DynModal is no different. With that said, if you wish to help make DynModal better and improve the user experience for everyone, we welcome bug reports and, if you are also a developer, you may also submit a pull request at any time.
Before submitting a bug request, however, please be sure to include the following:
- Please detail the current version of jQuery, Bootstrap, and DynModal that you are running
- Please detail the affected web browser(s), operating system(s), as well as web server(s)
- If possible, please include a JSFiddle example
- Finally, please provide a detailed overview of the problem you wish to have fixed, as well as possible steps that we may use to reproduce them on our end.
Contributing
If you would like to contribute to DynModal, please follow the following basic steps. Failure to do may result in your pull request being closed or you being asked to reformat the request.
- Rebase your branch against the master branch
- Run
npm installand verify that all dev dependencies are installed - Be very thorough in your commit detailing what feature you have added or what bug you have fixed
- If you have more than one commit, merge all of the commits together before submitting a pull request
- Just like the commit, please be thorough in your pull request GitHub post stating the feature you added or bug you fixed, as well as your reasoning for doing so
License
DynModal - Simple Typescript plugin for dynamically creating Bootstrap 4 modals Copyright (C) 2018 James D. Coon This program is free software: you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation, either version 3 of the License, or (at your option) any later version. This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details. You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program. If not, see <https://www.gnu.org/licenses/>. You may also view the full GNU/GPL v3 license by viewing the accompanying LICENSE file inside this master branch.