jquery-fsortable 
A fixed layout sortable plugin for jQuery UI.
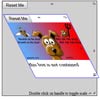
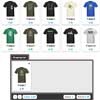
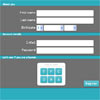
Demo
Check http://nighttrax.github.io/jquery-fsortable/ for a demo.
IMPORTANT NOTE
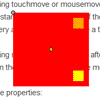
The jQuery UI sortable plugin (which fsortable builds upon) currently has 2 bugs that affect fsortable when working with connected sortables.
The first bug causes over and out events to not be triggered properly when using connected sortables. See http://bugs.jqueryui.com/ticket/9335 for more details.
The second bug causes change events to trigger on the sender list, rather than on the current list, when dragging an item from a connected sortable. See http://bugs.jqueryui.com/ticket/9760 for more details.
If you don't need connected sortables then you can use this plugin as is. However, if you do require that functionality, then please use the following repo until the fixes land upstream. https://github.com/NiGhTTraX/jquery-ui/tree/experimental
Usage
Include jquery-fsortable.js in your project and call $("#my-div").fsortable(). fsortable creates a sortable instance for you. You can call it on an existing instance by passing existingSortable: true in the options at creation time.
After you create the fsortable instance you can call methods on the underlying sortable instance by passing them through the .sortable() wrapper. The plugin will still fire sort instance just like a normal sortable plugin.
Creating a fixed layout
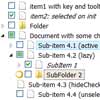
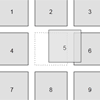
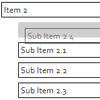
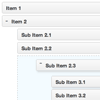
There's some necessary markup you need to use to let fsortable know about your layout. Since it assumes your sortable has a fixed capacity you need to tell it how many items it can hold. It takes that information from the HTML itself by counting the number of items in your sortable and the number of empty positions.
Any item that matches the items option of the sortable plugin will be counted as being part of the layout. Any item that has the emptyClass class will be counted as being a free slot. The sum of both will be the total capacity of the sortable.
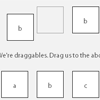
Let's take an example.
<div id="mysortable"> <div>Item 1</div> <div>Item 2</div> <div class="fsortable-empty"></div> <div>Item 3</div> </div>We've defined a layout with a total capacity of 4, that contains 3 items and 1 free slot. Once that free slot will be occupied (i.e. dragging a draggable over it) the fsortable will become full and it will be marked as being so by having the full class set on it.
If you need to change the size of the fsortable you can do so, but remember to call the refresh method on it so it recalculates the items and free slots.
To connect draggables with your fsortable you need to do the following.
$(".my-draggable").draggable({ connectToSortable: ".fsortable:not(.full)" });Note the :not(.full) selector. That tells the draggables to not connect with full fsortables.
Building
Fsortable uses the Grunt build system. To build Fsortable, you must have node.js installed and then run the following commands:
# Install the Grunt CLI. npm install -g grunt-cli # Clone the repository. git clone [email protected]:NiGhTTraX/jquery-fsortable.git cd jquery-fsortable # Install node module dependencies. npm install # Run the build task. gruntIf all went well, you will find a minified version of the plugin in the build/ folder.
Testing
Run grunt test to run the tests in PhantomJS or open tests/index.html to run them in your browser. Tests are written using the QUnit framework and the jQuery Event Unit Testing Helpers.
To enable coverage, place the resources/ and tests/ folders in your webserver and run the tests from there with the coverage option in QUnit checked (running coverage locally will throw a cross-domain error). Coverage is done using blanket.js.