react-audioplayer
A customizable HTML5 audio player for React.js
Features
- A ready-to-use web audio player for React.js
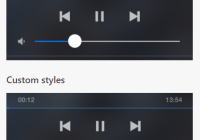
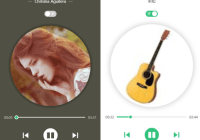
- Highly-customizable. You can change theme color, size, functions of this player as you want.
- Just one single component on the top to use (Almost no learning cost).
Install
- npm:
npm install react-audioplayer --save - yarn:
yarn add react-audioplayer
Usage
A simple example below.
import Audio from 'react-audioplayer'; // In your render() function: <Audio width={600} height={400} autoPlay={true} playlist={somePlaylist} />Acceptable props
| prop name | value type | default value | isRequired | explanation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| width | number | 400 | no | Width of the component (px) |
| height | number | fullPlayer ? 300 : 52 | no | Height of the component (px) |
| color | string | "#212121" | no | Theme color of the player |
| autoPlay | bool | false | no | Automatically playing when loaded |
| volumeOrientationDown | bool | false | no | Make the volume bar head downwards (make it true if the player is positioned at the very top of your webpage) |
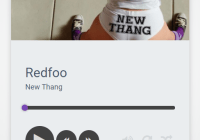
| fullPlayer | bool | false | no | If true, shows song image given in the playlist. Otherwise just shows the basic player |
| comment | bool | false | no | If true, enables comment function. When fullPlayer is false, this is forced to be false. You need to specify onCommentSubmit to handle user input |
| onCommentSubmit (text) | Function | null | no | When a user submits a new comment, this function will be invoked and the input content will be passed as an argument |
| playlist | array | null | yes | An array of song information objects, see below for details |
| style | object | null | no | A normal style object. For example, you can add border or boxShadow to the component. If you also set width or height here, it will override the one you set using width or height API |
playlist prop
playlist is an array of songObj, where
songObj = { name: string, // song name src: string, // song source address img: string, // (optional) song image source address comments: an commentObj array // (optional) comments to display of that song } commentObj = { time: number, content: string }songObj.img is required when fullPlay = true, songObj.comments is required when comment = true.
Manually control the state of the player in code
To play/pause/skip-to-next/skip-to-previous the player in code, four event listeners are added inside the <Audio /> component.
The name of these events are:
audio-playaudio-pauseaudio-skip-to-nextaudio-skip-to-previous
and a typical example:
class App extends React.Component { someMethod() { // Some code ... // This code can only be able to execute when the audio component is already mounted ReactDOM.findDOMNode(this.audioComponent).dispatchEvent(new Event('audio-play')); } render() { return ( <Audio width={600} height={300} playlist={playlist} // store a reference of the audio component ref={audioComponent => { this.audioComponent = audioComponent; }} /> ); } }As you can see in the example above, there are two steps:
- Store the audio component using ref
- Get the DOM node (ReactDOM.findDOMNode) and dispatch the event (dispatchEvent)
TODO
- Loading animation and optimisation
Development
$ git clone https://github.com/wenliangdai/react-audioplayer.git $ npm install $ npm startThen a localhost is open on port 8080.
ChangeLog
Details changes for each release are documented in the release notes or the ChangeLog.md file.
Need help or find a bug?
- github issues
- Email: [email protected]