navscroll-js
Installation
This package is available on npm.
Using npm:
npm install --save navscrollUsing yarn:
yarn add navscrollDirectly include it in html:
<script src="node_modules/navscroll/dist/navscroll.js"></script>When including it in html, it will automatically call `Vue.use` and also set a `NavScroll` property on the window object that you can use !
Features
This package was inspired by two other great packages: vue-scrollactive and vue-scrollto.
-
Scroll to an element inside a given container (if you only need this feature, got to the usage section below)
-
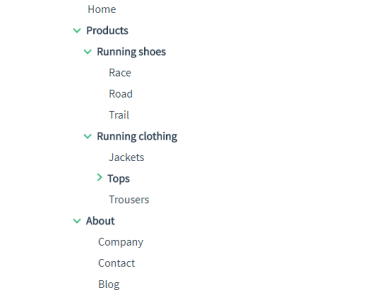
Highlights navigation items as you scroll based on the current visible section inside the scrolling container
-
Keeps track of added/removed navigation items inside a given wrapper element with a smart DOM observer
-
Uses
window.requestAnimationFrameto perform the animations for performance optimization. -
Supports animation cancelation
-
Easing done with the outstanding bezier-easing micro-library
-
Fully customizable behavior like easing or scroll axis by passing a configuration object
-
Uses passive event listeners when possible for better performance
-
Uses vanilla JS !
Be sure to check the live demo !
Usage
NavScroll.js can be used either as a vue component, a vue directive or programatically from your javascript.
In your JS:
import NavScroll from 'navscroll'; Vue.use(NavScroll); // This will register both a "navscroll" directive and component globally. You can rename as follow in your Vue instances: new Vue({ components: { 'new-name': NavScroll } // or directives: { 'new-name': NavScroll } })All options should be passed as a prop in the component, as binding value to the directive or as object when directly calling NavScroll methods.
Check out the Configuration section for more details about the available options.
You can set the defaults with
NavScroll.setDefaults({ container: 'body', duration: 500, easing: 'ease', offset: 0, cancelable: true, onDone: false, onCancel: false, scrollX: false, scrollY: true })As a Vue Component
<navscroll class="nav-scroll-items" container="#my-scrollable-container" item-selector=".item" active-class="active-element"> <a v-for="(entry,i) of entries" :key="i" :href="'#'+entry+'-target'" class="item">My nav item {{i}}</a> </navscroll>As a Vue Directive (on the wrapper)
<nav class="nav-scroll-items" v-navscroll:item="{ container: '#my-scrollable-container', activeClass: 'active-element' }"> <a v-for="(entry,i) of entries" :key="i" :href="'#'+entry+'-target'" class="item">My nav item {{i}}</a> </nav>As a Vue Directive (on the clickable navigation items)
<nav id="wrapper" ref="wrapper" class="nav-scroll-items"> <a v-for="(entry,i) of entries" :key="i" :href="'#'+entry+'-target'" class="item" v-navscroll="{ container: '#my-scrollable-container', activeClass: 'active-element' }">My nav item {{i}}</a> </nav>This will only attach the scrollTo function to the navigation items. If you also want the onScroll beahavior, then you have to explicitely call NavScroll.initObserver(this.$refs.wrapper, '.item', optionsObject) with the proper arguments (optionsObject would be the object passed as binding to the directives). NOTE: Be sure to call this function when both the navigation wrapper and the scrolling container are present in the DOM to properly register the handlers.
Programmatically
<nav id="wrapper" class="nav-scroll-items"> <a v-for="(entry,i) of entries" :key="i" :href="'#'+entry+'-target'" class="item">My nav item {{i}}</a> </nav>And in the script:
let navWrapper = document.getElementById('wrapper'); let options = { container: '#my-scrollable-container', activeClass: 'active-element' } // Call the following code when both the nav wrapper and the scrolling container are present in the DOM // This will register the scrollTo fn as the onlick handler on the nav items and also register the onScroll handler on the scrolling container. It will then observe for new/removed nav items inside the wrapper. NavScroll.initObserver(navWrapper, '.item', options) // If you only want the scrollTo behavior on your nav items, do this instead: [].slice.call(document.querySelectorAll('.item')).forEach(element => { let target = element.hash; let duration = 400; element.addEventListener('click', NavScroll.scrollTo.bind(null, target, duration, options)) }) // Another alternative import NavScroll from 'navscroll'; var options = { container: '#my-scrollable-container', easing: 'ease-in', offset: 60, cancelable: true, onDone: function() { // scrolling is done }, onCancel: function() { // scrolling has been cancelled }, scrollX: false, scrollY: true } var cancelScroll = NavScroll.scrollTo(targetElement, duration, options) // or alternatively inside your components you can use cancelScroll = this.$scrollTo(targetElement, duration, options) // to cancel scrolling you can call the returned function cancelScroll()You only need the scrollTo feature ?
If you only need the scrollTo feature just import the scroll-to.js script instead of the whole navscoll lib in your browser or module:
import ScrollTo from 'navcroll/dist/scroll-to'or in html:
<script src="/node_modules/dist/navscroll/scroll-to.js"></script>In browser environment, this will add the NavScrollTo function to the window object. The function has the following signature: NavScrollTo(targetElement, duration, options).
Configuration
All options are optional and have default values.
{ /** * The scrollable container. * It can be a selector string or the HTML element itself * * @default 'body' * @type {String|HTMLElement} */ container: 'body', /** * Selector that will be used to recognize the navigation items inside the navigation wrapper. * * @default 'scroll-item' * @type {String} */ itemSelector: '.scroll-item', /** * Class that will be applied to the menu item after the scroll animation. * * @default 'active' * @type {String} */ activeClass: 'active', /** * The target element/selector for the scrollTo method. Only used when registering * click handlers on the nav items. If the option is not set, registration will use * the href or the dataset.href of the registered nav item. * Alias: 'element' * * @default null * @type {String|HTMLElement} */ el: null, /** * The duration of the scroll animation * * @default 600 * @type {Number} */ duration: 600, /** * Your custom easing value for the click to scroll functionality. * It must be: * - a string with 4 values separated by commas in a cubic bezier format (ex: '.5,0,.35,1'). * - a string value among one of the following values: * 'ease', 'linear', 'ease-in', 'ease-out' or 'ease-in-out' * - an array of 4 values in a cubic bezier format (ex: [0.5, 0, 0.35, 1]). * * @example ".5,0,.35,1" * @default 'ease' * @type {String|Array} */ easing: "ease", /** * Whether to scroll on the X axis * * @default false * @type {Boolean} */ scrollX: false, /** * Whether to scroll on the Y axis * * @default true * @type {Boolean} */ scrollY: true, /** * Amount of space between top / left side of screen and the section to * highlight. * * @default 0 * @type {Number} */ offset: 0, /** * Threshold amount of space between left side of screen and the section to * highlight as the current one (for the onScroll handler). * * @default (2/3 of the X axis of the screen, calculated each time onScroll is called). Here's the formula: * ``` * Math.round( * (window.innerWidth || document.documentElement.clientWidth) / 3 * ) * 2 * ``` * @type {Number} */ onScrollOffsetX: undefined, /** * Threshold amount of space between top side of screen and the section to * highlight as the current one (for the onScroll handler). * * @default (2/3 of the Y axis of the screen, calculated each time onScroll is called). Here's the formula: * ``` * Math.round( * (window.innerHeight || document.documentElement.clientHeight) / 3 * ) * 2 * ``` * @type {Number} */ onScrollOffsetY: undefined, /** * Defines whether to track section changes when * clicking an item to scroll to its section. If set to true, * the scrolling listener will always keep track and change the active class * to the current section while scrolling, if false, the scrolling handler will be * removed temporarily from the scrolling container and the active class will be * immediately applied to the clicked menu item, ignoring the passed sections * until the scrolling is over. * * @default false * @type {Boolean} */ alwaysTrack: false, /** * Allow the scroll animation to be cancelled. * In that case, events like 'keyup' or 'touchmove' will cancel the animation * and scroll the content immediately to the target. * * @default 0 * @type {Boolean} */ cancelable: true, /** * Whether to stop the propagation of the click event on a menu item * * @default true * @type {Boolean} */ stopPropagation: true, /** * Callback called when scrolling is finished. * Also called when the scroll animation is cancelled (right after the onCancel callback). * * @default null * @type {Function} */ onDone: null, /** * Callback called when the scroll animation is cancelled. * * @default null * @type {Function} */ onCancel: null, /** * Whether to update window.location.hash when a link menu item with a href is clicked * * @default true * @type {Boolean} */ anchor: true, /** * Hash of the target section. * It will be applyed to window.location.hash if the `anchor` option is set to true. * * NOTE: If the clicked item or if the `clickedNavItem` option is set and the element has * a href or a data-href attribute, this attribute it will have priority to this option. * * @default null * @type {String} */ hash: null, /** * Enables/disables the scrolling when clicking in a menu item. * Disable if you'd like to handle the scrolling by your own. * * @default true * @type {Boolean} */ clickToScroll: true, /** * The reference to the navigation element that was clicked to trigger the scroll. * * @default null * @type {HTMLElement} */ clickedNavItem: null, /** * An array of navigation elements that can be clicked to trigger * a scroll to their target section. * * @default [] * @type {Array<HTMLElement>} */ navItems: [], }