topeka
topeka leverages react context, to create low friction input bindings for complex or nested values.
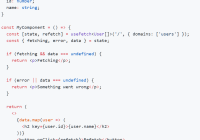
let eventValue = e => e.target.value; class App extends React.Component { constructor(){ super() state = { value: {} } } render(){ return ( <div> <BindingContext value={this.state.value} onChange={value => this.setState({ value }) } > <section> <Binding bindTo='name.first' mapValue={eventValue}> {events => <input type='text' placeholder='first name' {...events}/>} </Binding> <Binding bindTo='name.surname' mapValue={eventValue}> {events => <input type='text' placeholder='surname'{...events}/>} </Binding> <Binding bindTo='age' mapValue={e => parseInt(eventValue(e), 10)} > {events => <input type='number' placeholder='age' {...events}/>} </Binding> </section> </BindingContext> <div> <h5>current value: </h5> <pre>{JSON.stringify(this.state.value, null, 2) }</pre> </div> </div> ) } }The <Binding/> components operate on the assumption that they are rendering idiomatic React inputs, ie. controllable inputs. By default Bindings inject a value prop and an onChange callback to into their child. They then take care of updating with their surrounding BindingContext.
Composition
Bindings work with anything that accept a value and report a desired change in that value. Since BindingContext accept a value and fire onChange you can easily nest BindingContexts! Take the above example but with the name branch abstracted into its own component.
let eventValue = e => e.target.value; let Names = props => { return ( <BindingContext {...props}> <div> <Binding bindTo='first' mapValue={eventValue}> <input type='text' placeholder='first name' className='form-control'/> </Binding> <Binding bindTo='surname' mapValue={eventValue}> <input type='text' placeholder='surname' className='form-control'/> </Binding> </div> </BindingContext> ) } class App extends React.Component { constructor(){ super() state = { value: {} } } render(){ return ( <div> <BindingContext value={this.state.value} onChange={value => this.setState({ value }) } > <section> <Binding bindTo='name' mapValue={eventValue}> <Names/> </Binding> <Binding bindTo='age' mapValue={e => parseInt(eventValue(e), 10)} > <input type='number' placeholder='age'/> </Binding> </section> </BindingContext> <div> <h5>current value: </h5> <pre>{JSON.stringify(this.state.value, null, 2) }</pre> </div> </div> ) } }